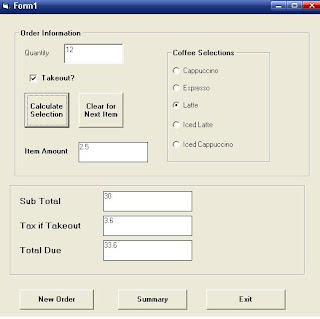
Private Sub Command1_Click()
Dim cap, esp, latte, icecap, icelatte As Boolean
Dim i_amount As Currency
Dim n_tax As Currency
Dim totaldue As Currency
Dim q_amount As Integer
Const n_cap = 1.5, n_esp = 2, n_latte = 2.5, n_icelatte = 3, n_icecap = 3.5, tax = 0.12
q_amount = Val(txtquan.Text)
If cappucino.Value = True Then
i_amount = q_amount * n_cap
lblamount.Caption = n_cap
lblsubtotal.Caption = i_amount
ElseIf espresso.Value = True Then
i_amount = q_amount * n_esp
lblamount.Caption = n_esp
lblsubtotal.Caption = i_amount
ElseIf late.Value = True Then
i_amount = q_amount * n_latte
lblamount.Caption = n_latte
lblsubtotal.Caption = i_amount
ElseIf icedlatte.Value = True Then
i_amount = q_amount * n_icelatte
lblamount.Caption = n_icelatte
lblsubtotal.Caption = i_amount
ElseIf icedcap.Value = True Then
i_amount = q_amount * n_icecap
lblamount.Caption = n_icecap
lblsubtotal.Caption = i_amount
End If
If checktakeout.Value = 1 Then
n_tax = tax * i_amount
Else
lbltax.Caption = 0
End If
totaldue = i_amount + n_tax
lbltax.Caption = n_tax
lbltotaldue.Caption = totaldue
End Sub
Private Sub cappucino_Click()
MsgBox "Cappucino $1.5"
End Sub
Private Sub Command2_Click()
txtquan = ""
lblamount = ""
lblsubtotal = ""
lbltax = ""
lbltotaldue = ""
End Sub
Private Sub Command3_Click()
txtquan = ""
lblamount = ""
lblsubtotal = ""
lbltax = ""
lbltotaldue = ""
End Sub
Private Sub Command5_Click()
End
End Sub
Private Sub Label3_Click()
End Sub
Private Sub espresso_Click()
MsgBox "Espresso $2.0"
End Sub
Private Sub icedcap_Click()
MsgBox "Iced Cappucino $3.5"
End Sub
Private Sub icedlatte_Click()
MsgBox "Iced Latte $3.00"
End Sub
Private Sub late_Click()
MsgBox "Latte $2.5"
End Sub
*This is one of my programming assignment in my computer course



